Treatment
Acute compartment syndrome
- Acute compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency.
- There is no non-surgical alternative.
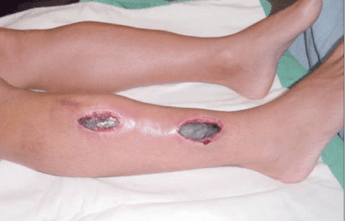
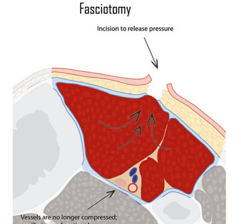
- The surgical intervention is fasciotomy, performed urgently. This involves opening the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and the fascia covering the compartment affected by this condition. Sometimes, the increase in volume may be such that it does not allow closure of the skin at the end of the procedure. In these cases, the reduction of volume is awaited postoperatively for wound closure, and in some cases, grafts or covering flaps may be necessary for an optimal result.
*The clinical outcome of Acute Compartment Syndrome is correlated with the timeliness of treatment.
Chronic compartment syndrome
Non-surgical treatment
Physical therapy, insoles, anti-inflammatory drugs may have some effect in reducing symptoms.
However, the symptoms are still related to physical activity, and a change in sports activity or training method can be considered. Some athletes may experience worse symptoms when training on certain surfaces (hard concrete or synthetic), in which case the symptoms may decrease by changing the training surface or increasing footwear elasticity and absorption using insoles or gel inserts.
Surgical treatment
If non-surgical treatment fails, surgery is the only alternative.
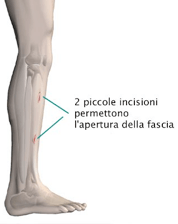
The surgical intervention is similar to that used for acute treatment, as it must aim at opening the fascia.
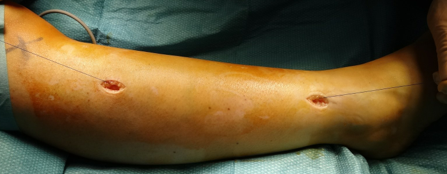
- Usually, the surgical incision is more limited.
- Mini-invasive surgical techniques allow for surgical accesses less than 2 cm, allowing for fascia opening without compromising the functionality and aesthetics of the affected limb.